In the ever-evolving landscape of employee benefits, a noticeable shift is occurring in the perception and necessity of voluntary benefits. As workplaces adapt to the changing needs and expectations of their diverse populations, voluntary benefits are emerging as a crucial component of a comprehensive employee well-being strategy.

What are voluntary benefits?
Voluntary benefits programs act as a perk of employment and are designed to provide benefits when employees need them the most. As the name suggests, these benefits are not mandatory and are often offered at a group rate. With the large array of products and services to select from, many employees find voluntary benefits to be especially attractive, as they can build a program suited to their specific needs. The four main categories and use cases are health and wellness, personal benefits, financial wellness, and financial security. Some examples of these benefits include, critical illness insurance, legal, identity theft, pet insurance, paid disability, tuition assistance, and more. They can be used to enhance quality of life either directly or through the promise of future security.
Shift in the necessity of voluntary benefits
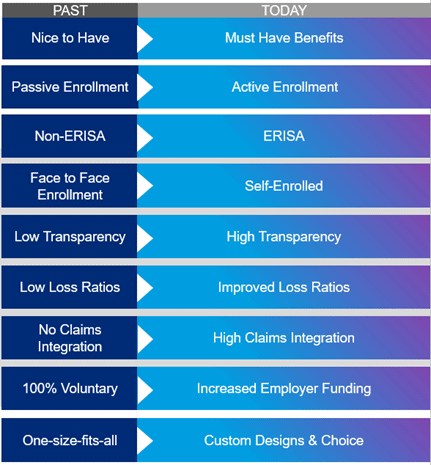
The evolution of voluntary benefits is a driving factor behind the growing popularity of alternative funding solutions. When considering the historical characteristics of these products, the last decade reflects a dramatic change. Traditionally, the benefit packages were one-size-fits-all with no flexibility for the varying needs of employees. Previously, these benefits were secondary solutions to be used at the employees’ convenience. Enrollment was passive and they were not considered to be products of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). To acquire these benefits, it was necessary to meet face-to-face with an advisor to learn about and enroll for each offering. Additionally, lack of transparency into claims experience, loss ratios, and commissions had been characteristic of the industry. Today, we see that the modern workforce is diverse with employees spanning multiple generations, each with unique preferences and priorities. These benefits now follow the core benefits in the enrollment guide to illustrate how they complement the medical benefits. They have evolved so that they can be self-enrolled and are treated like other ERISA programs.
Factors contributing to the growing importance of voluntary benefits
Traditional, one-size-fits-all benefit packages no longer resonate with the varying needs of today’s employees. As a result, the demand for voluntary benefits has surged, offering employees the flexibility to tailor their benefits to align with their circumstances. Factors of the increased prioritization of voluntary benefits include the rise of work-life balance, health and financial wellness, technology and administration, and the declining number of Human Resources (HR) members.
Work-life balance has become a focal point for employees seeking holistic well-being. Voluntary benefits, such as flexible work schedules, remote work options, and wellness programs, play a pivotal role in supporting employees’ efforts to balance their professional and personal lives.
With the increase of high deductible health plans and the need to have products wrapped around the core benefits, voluntary benefits such as accident, critical illness, and hospital indemnity coverages have become key components of the overall core benefits structure. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of health and financial stability. Voluntary benefits, such as telemedicine services, income protection, and critical illness coverage, have gained significance in response to the challenges posed by the pandemic.
Additionally, the advancement of technology has enabled the administration of voluntary benefits to become more streamlined. Digital enrollment platforms and online access made it easier for employees to choose and manage their benefits. Individuals now have a better understanding of the benefits, and face-to-face interaction is no longer necessary. Self-enrollment is the new norm.
Concurrently, there is a trend in the market in which staffing within HR is declining. Where there used to be several staff members, companies are now asking HR teams to do more with less, including funding. HR managers are looking towards captives for funds to help support employee programs.
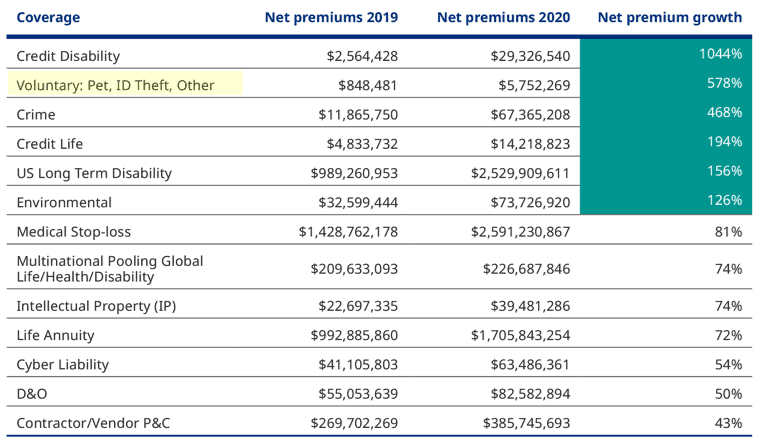
Growth of captive programs
A captive insurance company is a subsidiary established by an organization to provide insurance coverage to its parent company and related entities. They can offer several advantages to employers and employees, including HR departments, through improved transparency, effective risk management, cost control, and the customization of insurance programs.
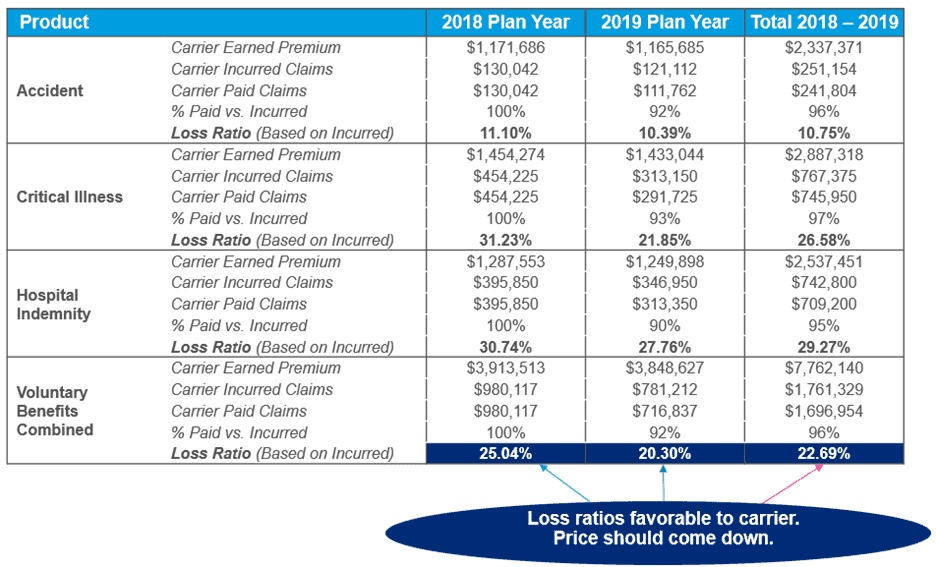
While voluntary benefits offer improvements in transparency, loss ratios, and claims integration, the problem has not been completely solved. Typical voluntary benefits loss ratios are 25%-30%. To combat this issue, captives play a large role in allowing and requiring employers to be engaged with the program. They offer organizations greater control over their insurance programs, allowing them to tailor coverage to the specific needs of their workforce.
Organizations are continually exploring innovative risk mitigation strategies, and captive structures can be part of a broader risk management approach. They provide a structured approach to risk management. By retaining certain risks within the captive, organizations can have more control over their risk exposure and potentially reduce reliance on traditional insurance markets.
They may also contribute to more stable and predictable costs for HR departments. By retaining risks within the captive, organizations can avoid some of the fluctuations in premium costs associated with traditional insurance markets.
The following chart illustrates actual claims experience for a real client before implementing the captive program.
How can Marsh McLennan Agency help?
To meet the evolving needs of their workforce, forward-thinking organizations are strategically integrating voluntary benefits into their overall benefits packages. Marsh McLennan Agency (MMA) offers BeneCap, a voluntary benefits captive solution. BeneCap is designed to grow an employer’s captive by integrating 100% employee-paid lines of coverage with their existing risk management strategy. The goal is to drive the loss ratios up so that employees receive greater benefits and, if there are still excess premium dollars, provide funding to benefit the employees.
To determine the appropriate funding strategy, a 360° Diagnostic Assessment is conducted to analyze current benefit plans, technologies, and communications. This comprehensive analysis allows MMA to identify opportunities to enhance programs, streamline administration, reduce costs, and improve the employee experience. For more information, contact [email protected] or visit https://mmaeast.com/captive-solutions/.